Shaft Torsion Stress Calculator and Equations
Mechanics of Materials Table of Content
In solid mechanics , torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torque . It is expressed in newton meters(N·m) or foot-pound force (ft·lbf). In sections perpendicular to the torque axis, the resultant shear stress in this section is perpendicular to the radius.
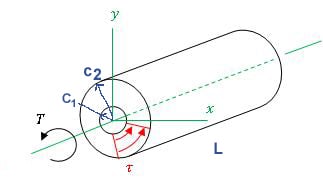
Shear stress is zero on the axis passing through the center of a shaft and maximum at the outside surface of a shaft. On an element where shear stress is maximum, normal stress is 0. This element where maximum shear stress occursis oriented in such a way that its faces are either parallel or perpendicular to the axis of the shaft as shown in the figure. To obtain stress in other orientations, plane stress transformation is needed for shear stresses found with this calculator.
Related:
Structural Beam Deflection and Stress Formula and Calculation
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
List of Equations:
Description |
Symbol |
Equation |
Shear stress |
τ |
|
Angle of twist |
θ |
|
Maximum shear stress |
τ max |
|
Polar moment of inertia of solid shaft |
J |
|
Polar moment of inertia of hollow shaft |
J |
|
Power |
P |
P = [(T/12) x w]/5252 |
Symbol |
Description |
T |
Torque to be transmitted |
J |
Polar moment of inertia |
p |
Radial distance to center of shaft |
c1 |
Hollow shaft inner radius |
c2 |
Shaft outer radius |
L |
Length of the shaft |
G |
Modulus of rigidity |
w |
Rotation speed |
P |
Power |
K |
Stress concentration factor |
Related
- Torsion Spring Design Formula and Calculator
- Torsion in Thin-Walled Noncircular Shells Calculator
- Torsional Deflection of Shaft
- Double Y Section with Concentrated Intermediate Torsional Loading Per. Roarks Formulas
- Hat Section Intermediate Torsion Applied No 3 Roarks Formulas for Stress and Strain Equations and Calculator
- Combined Loading on Circular Shaft in Direct Compression and Torsion Stress Equation and Calculator Circular Shaft in Direct Compression and Torsion Equation and Calculator:
- Loading on Circular Shaft in Direct Tension and Torsion Stress Equation and Calculator Combined Loading on Circular Shaft in Direct Tension and Torsion Equation and Calculator:
- Shaft Torsional Deflection and Rigidity Formulas and Calculator
- Cylinder Stress and Deflection with Applied Torsion
- Torsional Deformation and Stress Solid Elliptical Section Equations and Calculator
- Torsional Deformation and Stress Solid Rectangular Section Equations and Calculator
- Torsional Deformation and Stress Circular Segmental Section Equations and Calculator
- Torsional Deformation and Stress Eccentric Hollow Circular Section Equations and Calculator
- Torsional Deformation and Stress Hollow Elliptical Section Equations and Calculator
- Torsion Applied Deformation and Stress of any elongated section with axis of symmetry OX; Equations and Calculator
- Torsional Deformation and Stress of a Cross Shaft Equations and Calculator
- Power Transmission Shaft Design Formulas and Calculator for Torsional Stress, Deflection Calculator for Stress and Tensile or Compressive Stress.