Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Charts and Equation
Thermodynamics Directory
Heat Transfer Directory
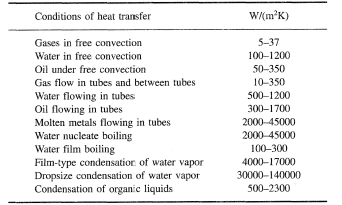
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart:
The heat transfer coefficient is the proportionality coefficient between the heat flux and the thermodynamic driving force for the flow of heat (i.e., the temperature difference, ΔT):
h = q / (Ts - K)
where:
q: amount of heat required (Heat Flux), W/m2 i.e., thermal power per unit area, q = d\dot{Q}/dA
h: heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2 K)
Ts = Solid Surface temperature
K = Surrounding fluid area Temperature
It is used in calculating the heat transfer, typically by convection or phase transition between a fluid and a solid. The heat transfer coefficient has SI units in watts per squared meter kelvin: W/(m2K). Heat transfer coefficient is the inverse of thermal insulance. This is used for building materials (R-value) and for clothing insulation.
Related Resources:
- Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient - Heat Transfer
- Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Thermodynamics
- Convective Heat Transfer Convection Equation and Calculator
- Thermal Conductivity Conversions
- Thermal Conductivity of Gases
- Thermal Conductivity of Common Metals and Alloys
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Pipes and Tubes
Types |
Application |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient - U - |
|
| W/(m2 K) | Btu/(ft2 oF h) | ||
| Tubular, heating or cooling | Gas at atmospheric pressure inside and outside tubes | 5 - 35 | 1 - 6 |
| Gas at high pressure inside and outside tubes | 150 - 500 | 25 - 90 | |
| Liquid outside (inside) and gas at atmospheric pressure inside (outside) tubes | 15 - 70 | 3 - 15 | |
| Gas at high pressure inside and liquid outside tubes | 200 - 400 | 35 - 70 | |
| Liquids inside and outside tubes | 150 - 1200 | 25 - 200 | |
| Steam outside and liquid inside tubes | 300 - 1200 | 50 - 200 | |
| Tubular, condensation | Steam outside and cooling water inside tubes | 1500 - 4000 | 250 - 700 |
| Organic vapors or ammonia outside and cooling water inside tubes | 300 - 1200 | 50 - 200 | |
| Tubular, evaporation | steam outside and high-viscous liquid inside tubes, natural circulation | 300 - 900 | 50 - 150 |
| steam outside and low-viscous liquid inside tubes, natural circulation | 600 - 1700 | 100 - 300 | |
| steam outside and liquid inside tubes, forced circulation | 900 - 3000 | 150 - 500 | |
| Air-cooled heat exchangers | Cooling of water | 600 - 750 | 100 - 130 |
| Cooling of liquid light hydrocarbons | 400 - 550 | 70 - 95 | |
| Cooling of tar | 30 - 60 | 5 - 10 | |
| Cooling of air or flue gas | 60 - 180 | 10 - 30 | |
| Cooling of hydrocarbon gas | 200 - 450 | 35 - 80 | |
| Condensation of low pressure steam | 700 - 850 | 125 - 150 | |
| Condensation of organic vapors | 350 - 500 | 65 - 90 | |
| Plate heat exchanger | liquid to liquid | 1000 - 4000 | 150 - 700 |
| Spiral heat exchanger | liquid to liquid | 700 - 2500 | 125 - 500 |
| condensing vapor to liquid | 900 - 3500 | 150 - 700 | |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Heat Exchangers
Heaters (no phase change) |
||
| Hot Fluid | Cold Fluid | Overall U (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Steam | Air | 10 – 20 |
| Steam | Water | 250 – 750 |
| Steam | Methanol | 200 – 700 |
| Steam | Ammonia | 200 – 700 |
| Steam | Aqueous solutions | 100 – 700 |
| Steam | Light hydrocarbons (viscosity < 0.5 cP) |
100 – 200 |
| Steam | Medium hydrocarbons (0.5 cP < viscosity < 1 cP) |
50 – 100 |
| Steam | Heavy hydrocarbons (viscosity > 1) |
6 – 60 |
| Steam | Gases | 5 – 50 |
| Dowtherm | Gases | 4 – 40 |
| Dowtherm | Heavy oils | 8 – 60 |
| Flue gas | Aromatic hydrocarbon and steam | 5 – 10 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Industrial Evaporators
Evaporators |
||
| Hot Fluid | Cold Fluid | Overall U (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Steam | Water | 350 – 750 |
| Steam | Organic solvents | 100 – 200 |
| Steam | Light oils | 80 – 180 |
| Steam | Heavy oils (vacuum) | 25 – 75 |
| Water | Refrigerant | 75 – 150 |
| Organic solvents | Refrigerant | 30 – 100 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Industrial Coolers
Coolers (no phase change) |
||
| Cold Fluid | Hot Fluid | Overall U (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Water | Water | 150 – 300 |
| Water | Organic solvent | 50 – 150 |
| Water | Gases | 3 – 50 |
| Water | Light oils | 60 – 160 |
| Water | Heavy oils | 10 – 50 |
| Light oil | Organic solvent | 20 – 70 |
| Brine | Water | 100 – 200 |
| Brine | Organic solvent | 30 – 90 |
| Brine | Gases | 3 – 50 |
| Organic solvents | Organic solvents | 20 – 60 |
| Heavy oils | Heavy oils | 8 – 50 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Industrial Condensers
Condensers |
||
| Cold Fluid | Hot Fluid | Overall U (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Water | Steam (pressure) | 350 -750 |
| Water | Steam (vacuum) | 300 – 600 |
| Water or brine | Organic solvent (saturated, atmospheric) | 100 – 200 |
| Water or brine | Organic solvent ( atmospheric, high non-condensables) | 20 – 80 |
| Water or brine | Organic solvent (saturated, vacuum) | 50 – 120 |
| Water or brine | Organic solvent (vacuum, high non-condensables) | 10 – 50 |
| Water or brine | Aromatic vapours (atmospheric with non-condensables) | 5 – 30 |
| Water | Low boiling hydrocarbon (atmospheric) | 80 – 200 |
| Water | High boiling hydrocarbon (vacuum) | 10 – 30 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Various Fluids
no phase change |
|
| Fluid | Film Coefficient (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Water | 300 – 2000 |
| Gases | 3 – 50 |
| Organic Solvents | 60 – 500 |
| Oils | 10 – 120 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Condensing Fluids
Condensing |
|
| Fluid | Film Coefficient (BTU/hr-ft2 -F) |
| Steam | 1000 – 3000 |
| Organic Solvents | 150 – 500 |
| Light Oils | 200 – 400 |
| Heavy Oils (vacuum) | 20 – 50 |
| Ammonia | 500 – 1000 |
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient Table Chart Various Fluids (Liquids and Gasses)