Related Resources: civil engineering
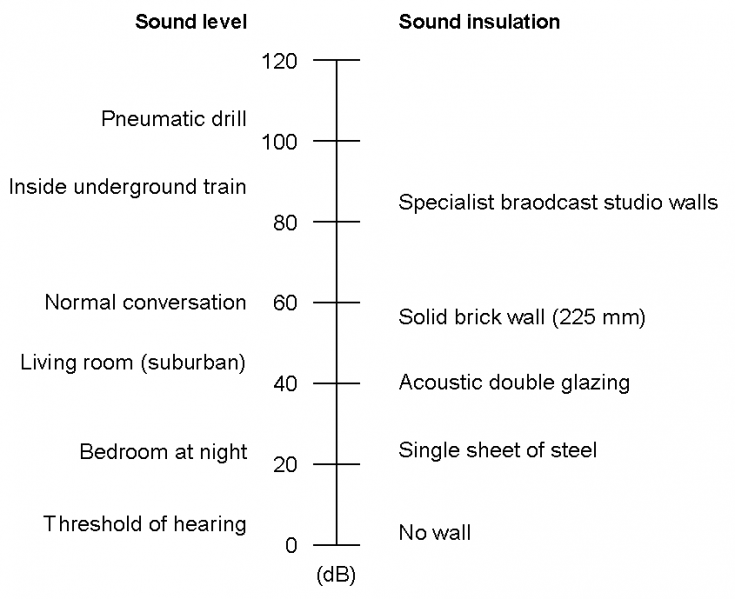
Acoustic Sound Pressure Level Chart
Civil Engineering Design & Applications
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average, or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone. The SI unit for sound pressure p is the pascal (symbol: Pa).
Examples of sound pressure in air at standard atmospheric pressure Source of sound Sound pressure* ( Pa ) Sound level ( dB SPL )
| Shockwave (distorted sound waves > 1 atm ; waveform valleys are clipped at zero pressure) |
>101,325 | >194 |
| Theoretical limit for undistorted sound at 1 atmosphere environmental pressure |
101,325 | 194 |
| Stun grenades | 6,000–20,000 | 170–180 |
| Simple open-ended thermoacoustic device | 12,619 | 176 |
| .30-06 rifle being fired 1 m to shooter's side | 7,265 | 171 |
| Rocket launch equipment acoustic tests | 4000 | 165 |
| LRAD 1000Xi Long Range Acoustic Device at 1 m | 893 | 153 |
| Jet engine at 1 m | 632 | 150 |
| Threshold of pain | 63.2 | 130 |
| Vuvuzela horn at 1 m | 20 | 120 |
| Risk of instantaneous noise-induced hearing loss | 20 | 120 |
| Jet engine at 100 m | 6.32–200 | 110–140 |
| Non-electric chainsaw at 1 m | 6.32 | 110 |
| Jack hammer at 1 m | 2 | 100 |
| Traffic on a busy roadway at 10 m | 0.2–0.632 | 80–90 |
| Hearing damage (over long-term exposure, need not be continuous) | 0.356 | 85 |
| Passenger car at 10 m | (2–20)×10 −2 | 60–80 |
| EPA -identified maximum to protect against hearing loss and other disruptive effects from noise, such as sleep disturbance, stress, learning detriment, etc. |
6.32×10 −2 | 70 |
| Handheld electric mixer | 65 | |
| TV (set at home level) at 1 m | 2×10 −2 | 60 |
| Washing machine , dishwasher | 42–53 | |
| Normal conversation at 1 m | (2–20)×10 −3 | 40–60 |
| Very calm room | (2–6.32)×10 −4 | 20–30 |
| Light leaf rustling, calm breathing | 6.32×10 −5 | 10 |
| Auditory threshold at 1 kHz | 2×10 −5 | 0 |
*All values listed are the effective sound pressure unless otherwise stated.