Belleville Spring Washer Equation and Calculator
Springs Washer Belleville Equation
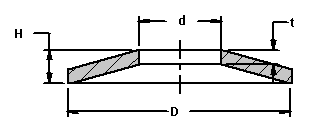
A Belleville spring or washer is formed into a conical or cone shaped geometry. The slight or aggressive conical shape gives the washer a spring characteristic and action. Belleville washers are typically used as springs where the spring action is used to apply a pre-load or flexible quality to a bolted joint. The equations below will determine the various characteristics including the applied load of a Belleville spring or washer.
Springs Washer Belleville Equation / Formula
Force at Maximum Spring Deflection and Limit Deflection:
Preview: Force at Maximum Spring Deflection and Limit Deflection Calculator
Equations used in above calculator
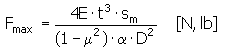
Where:
E = Spring modulus of elasticity [Pa, psi]
t = Spring material thickness [mm, in]
sm = Total or limit of spring deflection [mm, in]
µ = Poisson's ratio
α = calculation coefficient (see equation below)
D = outside spring diameter [mm, in]
Force Exerted by the Spring at s Deflection:
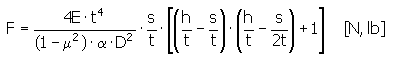
Where:
E = spring modulus of elasticity [Pa, psi]
t = spring material thickness [mm, in]
s = Design or working deflection of a spring [mm, in]
µ = Poisson's ratio
α = calculation coefficient
D = outside spring diameter [mm, in]
h = unloaded height of truncated cone of free spring [mm, in]
Maximum Pressure Stress in Spring at s Deflection:
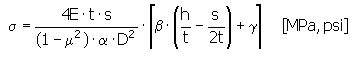
Where:
E = spring modulus of elasticity [MPa, psi]
t = spring material thickness [mm, in]
s = working deflection of a spring [mm, in]
= Poisson's ratio
α = calculation coefficient
D = outside spring diameter [mm, in]
β = calculation coefficient
h = unloaded height of truncated cone of free spring [mm, in]
γ = calculation coefficient
Diameter Ratio
![]()
Where:
D = outer spring diameter [mm, in]
d = inner spring diameter [mm, in]
Calculation coefficient α
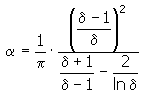
Calculation coefficient β
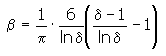
Calculation coefficient γ
![]()
Limit Washer Deflection
![]()
Where:
h = unloaded height of truncated cone of free spring [mm, in]
Unloaded height of truncated cone of free spring
h = H - t [mm, in]
Where:
H = unloaded spring height [mm, in]
t = spring material thickness [mm, in]
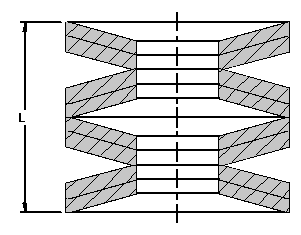
Total Springs in a Set or Stack up
![]()
Where:
n = spring number in a set with unidirectional mounting
i = spring number in a set with opposite mounting or number of sets with unidirectional mounting in a set with combined mounting
Stroke of Deflection of a Spring Set (Stack up)
![]()
Where:
i = spring number in a set with opposite mounting or number of sets with unidirectional mounting in a set with combined mounting
s = working deflection of a spring [mm, in]
Force Exerted by a Spring Set (Stack up)
![]()
Where:
n = spring number in a set with unidirectional mounting
F1 = force exerted by one washer [N, lb]
Height of Spring Stack up Unloaded
![]()
Where:
i = spring number in a set with opposite mounting or number of sets with unidirectional mounting in a set with combined mounting
h = unloaded height of truncated cone of free spring [mm, in]
n = spring number in a set with unidirectional mounting
t = spring material thickness [mm, in]
Height of Loaded Spring Stack up
![]()
L0 = Height of spring set in unloaded state [mm, in]
z = stroke (deflection) of spring set [mm, in]
Related
- Design Equations of Belleville Washer Springs
- Leaf Spring Design and Engineering Strength of Materials
- Constant Force Spring Design and Equations
- Coil Spring Engineering Design Application
- Helical Compression Spring Design Equations and Calculator
- Compression Spring Assembly Operating Life and Reliability Equations and Calculator
- Shock Loading Helical Springs Formulas and Calculator
- Helical Spring Fatigue Loading and Factor of Safety Formulas and Calculator
- Series and Parallel Spring Forces Calculator