Related Resources: calculators
Parshall Flume Flow Measurement Equations and Calculator
Civil Engineering and Design
Fluids Engineering and Design
Parshall Flume Flow Measurement Equations and Calculator
Preview Parshall Flume Calculator
The Parshall flume is widely used for measuring open channel wastewater flows. It performs well when head losses must be kept to a minimum and when there are high amounts of suspended solids.
The Parshall flume is constructed with a converging upstream section, a throat, and a diverging downstream section. The walls of the flume are vertical, but the floor of the throat section drops. The length, width, and height of the flume are essentially predefined by the anticipated flow rate.
The throat geometry in a Parshall flume has been designed to force the occurrence of critical flow at that point. Following the critical section is a short length of supercritical flow followed by a hydraulic jump. This design eliminates any dead water region where debris and silt can accumulate (as are common with flattopped weirs).
The discharge relationship for a Parshall flume is given for submergence ratios of Hb/Ha up to 0.7. Above 0.7, the true discharge is less than predicted by Eq. 1. Values of K are given in Table 1, although using a value of 4.0 is accurate for most purposes.
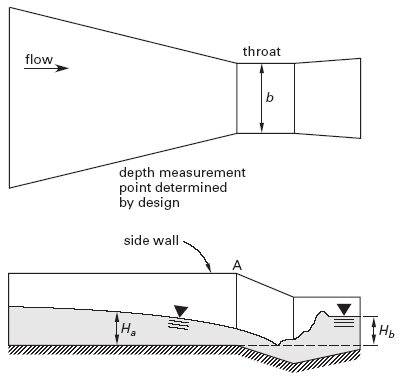
Figure 1 Parshall Flume
Eq.1
Q = K b Han
Eq. 2
n = 1.522 b0.026
Where:
Q = Flow rate, cfs, m3
K = See Table 1 below
Ha = Height, ft, m
b = Throat Width, ft, m
Above a certain tailwater height, the Parshall flume no longer operates in the free-flow mode. Rather, it operates in a submerged mode. A very high tailwater reduces the flow rate through the flume. Equation 1 predicts the flow rate with reasonable accuracy, however, even for 50–80% submergence (calculated as Hb/Ha). For large submergence, the tailwater height must be known and a different analysis method must be used.
Table 1 Parshall Flume Width and K-Values
|
b
ft |
b
m |
K
|
|
0.25
|
0.076
|
3.97
|
|
0.50
|
0.15
|
4.12
|
|
0.75
|
0.229
|
4.09
|
|
1.0
|
0.305
|
4.00
|
|
1.5
|
0.46
|
4.00
|
|
2.0
|
0.61
|
4.00
|
|
3.0
|
0.92
|
4.00
|
|
4.0
|
1.22
|
4.00
|
(Multiply ft by 0.3048 to obtain m.)
Reference
Civil Engineering Reference Manual, Fifteenth Edition, Michael R. Lindeburg, PE
Related
- Proportional Weirs Equations and Calculator
- Weir Flow Rectangular Open Channel Water Flow Calculator and Formula
- Trapezoidal Weirs Flow Formula and Calculator
- Triangular Weirs Flow Formula and Calculator
- Water Flow Kinetic Force in Flow Around Submerged Object Calculator and Equation.
- Dam's Spillway (overflow spillway) Flow Formula and Calculator
- Flow Through a Sluice Gate Formula and Calculator
- Flow over Channel Rise Hump Formula
- Weir Flow Rectangular Open Channel Water Flow Calculator and Formula
- Pipe Flow with Gradual Size Enlargement Formula and Calculator
- Fluid Characteristics Chart Table | Fluids Data, Fluids Density | Vapor Pressure | Kinematic Viscosity
- Fluid Characteristics Chart Table #2 | Fluids Data, Fluids Density